Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
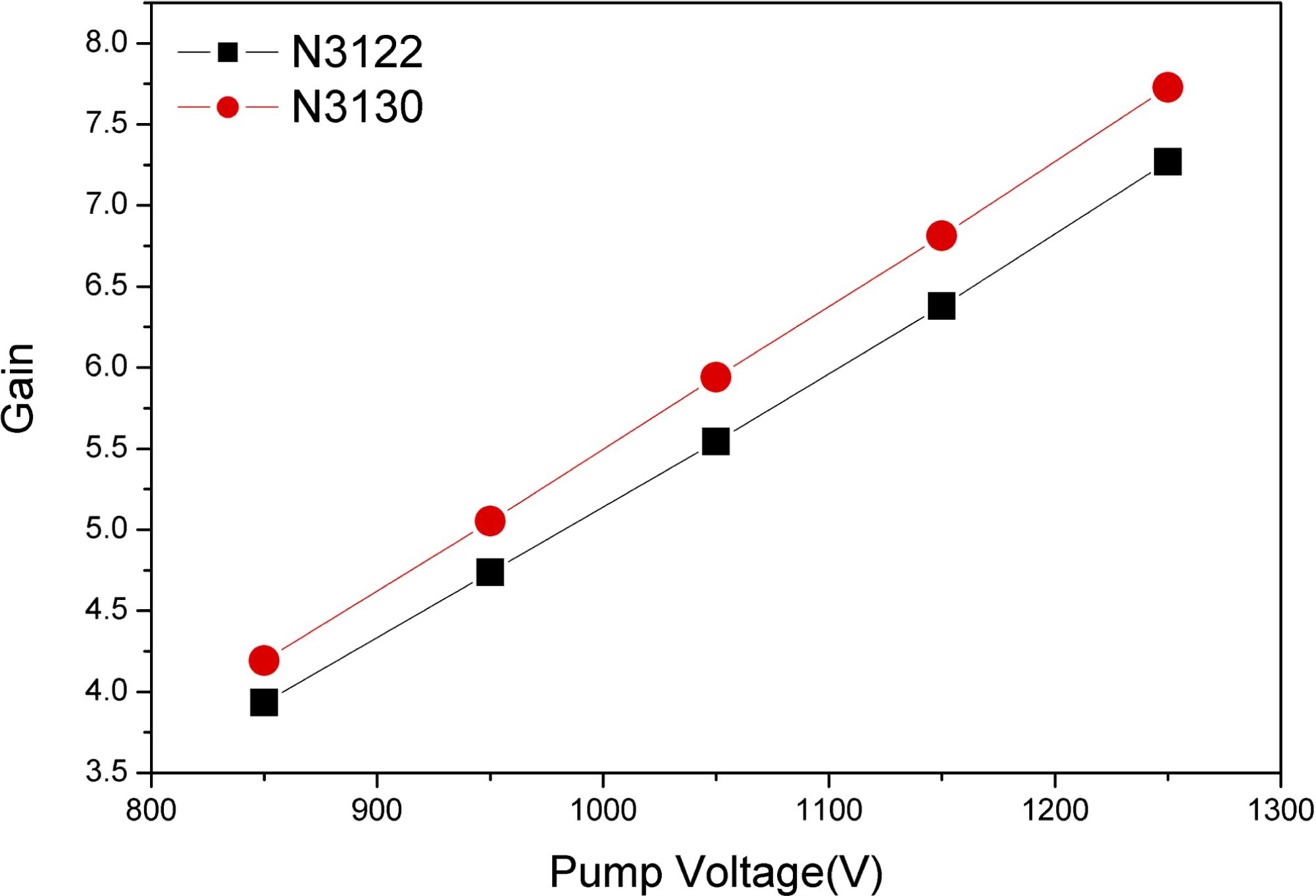
Large aperture Nd:phosphate laser glass is a key optical element for an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) facility. N31, one type of neodymium doped phosphate glasses, was developed for high peak power laser facility applications in China. The composition and main properties of N31 glass are given, together with those of LHG-8, LG-770, and KGSS- 0180 Nd:phosphate laser glasses, from Hoya and Schott, and from Russia. The technologies of pot melting, continuous melting, and edge cladding of large size N31 phosphate laser glass are briefly described. The small signal gain profiles of N31 glass slabs from both pot melting and continuous melting at various values of the pumping energy of the xenon lamp are presented. N31 glass is characterized by a stimulated emission cross section of 3:8 � 10??20 cm2 at 1053 nm, an absorption coefficient of 0.10–0.15% cm??1 at laser wavelength, small residual stress around the interface between the cladding glass and the laser glass, optical homogeneity of �2 � 10??6 in a 400 mm aperture, and laser damage threshold larger than 42 J/cm2 for a 3 ns pulse width at 1064 nm wavelength.
neodymium phosphate laser glass large aperture glass ICF facility High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2014, 2(1): 010000e1
Author Affiliations
Abstract
A simple and efficient method for the synthesis of water-soluble NdF3 and NdF3:Ba2+ nanocrystals under hydrothermal conditions is established. The method involves the coating of the nanocrystals with a layer of hydrophilic polymer polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). The as-prepared products are characterized by powder X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electronic microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and photoluminescence spectroscopy. The PVP coating transforms the nanocrystals into a biocompatible material and improves the fluorescence intensity of NdF3 in the near infrared (NIR) region. The morphology of the nanoparticles changes, whereas the fluorescence intensity of NdF3 in the NIR region increases when a small amount of Ba2+ is doped into the NdF3/PVP nanoparticles.
160.0160 Materials 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.4236 Nanomaterials 160.4670 Optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(2): 021602
中国科学院 上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
在概述国内外高功率激光钕玻璃的发展及其主要性质的基础上,重点论述了上海光学精密机械研究所在大口径N31高功率激光钕玻璃半连续熔炼工艺、连续熔炼工艺、包边工艺等方面的研究进展。报道了半连续熔炼工艺制备的不同Nd2O3浓度N31钕玻璃的光吸收损耗和荧光寿命及小信号增益系数,并给出了这些钕玻璃坯片小信号增益系数的波动范围。通过对半连续熔炼和连续熔炼工艺制备的N31激光钕玻璃主要性能的比较,证明连续熔炼工艺制备的N31钕玻璃的主要性能指标与半连续熔炼的性能相当。对于400 mm大口径N31钕玻璃坯片的包边进行了模拟考核,结果表明,采用现有包边工艺的钕玻璃可以承受1 000次高功率氙灯辐射。
高功率激光 钕玻璃 大口径 惯性约束聚变 high power laser neodymium laser glass large aperture inertial confinement fusion 强激光与粒子束
2011, 23(10): 2560
1 中国科学院 上海光学精密机械研究所,上海 201800
2 华南理工大学,广东 广州 510641
概述了激光玻璃发明近五十年的发展历史,重点阐述了中国激光钕玻璃的研究发展历程,国内外高功率磷酸盐激光钕玻璃的性质,以及它们在国内外大型激光核聚变装置中的应用。介绍了用于激光产生与放大的掺稀土多组分玻璃光纤。
激光玻璃 惯性约束聚变 玻璃光纤 稀土离子
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所,上海 201800
2 中国科学院研究生院,北京 100039
3 宁波大学信息科学与工程学院,宁波 315211
熔制了掺铒碲铌玻璃样品(100-X)TeO2-XNb2O5(X=5,10,15,20mol%),测试了其密度、折射率、转变温度、析晶温度、维氏机械强度、吸收光谱、荧光光谱、荧光寿命等参量。利用Judd-Ofelt和McCumber理论分别计算了铒离子强度参量Ωt(t=2,4,6)和受激发射截面σemi的大小,研究了掺铒碲铌玻璃样品光谱参量对Nb2O5成分的依赖性,并与典型的碲锌钠玻璃(75TeO220ZnO-5Na2O)在热学、机械强度、光谱性质和放大品行四个方面进行了比较.
掺铒碲铌玻璃 光谱性质 机械强度 宽带光纤放大器 Er3+-doped TeO2-Nb2 Spectroscopy Mechanical strength Broadband optical amplifier
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laser Glass Laboratory, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800
2 Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049
3 College of Information Science and Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211
Optically transparent Er3+-doped tellurite-based nanocrystallized glasses with the composition of 70TeO2-15Li2O-15Nb2O5-0.5Er2O3 (mol) have been prepared by a conventional melting quenching and the subsequent heat treatment processes. The sizes of grown nanocrystals in glass matrix appear to be 35-50 nm from the X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurement. The microhardness measurement shows that the Vickers hardness values of the nanocrystallized tellurite glasses are larger (33%-62%) than those in the base glass. The Raman spectra imply that the maximum phonon energy of the based glass decreases and shifts from 668 to 638 /cm after heat-treatment. Visible upconversion luminescence and infrared luminescence of the base glass and heat-treated glasses under 980-nm laser diode (LD) excitation are investigated. The 524-, 546- and 656-nm upconversion intensities by 980-nm pumping increase significantly.
160.4670 optical materials 160.5690 rare earth doped materials 300.6280 spectroscopy fluorescence and luminescence 160.2750 glass and other amorphous materials Chinese Optics Letters
2006, 4(1): 0136
Author Affiliations
Abstract
中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理国家实验室, 上海 201800
Organosilicone composite antireflective (AR) coating was successfully prepared for Ti-sapphire crystals by sol-gel process from precursors of tetraethoxysilane [Si(OC2H5)4, TEOS] and methyltriethoxysilane [CH3Si(OC2H5)3, MTEOS]. This AR coating possessed prominent AR effect within the output waveband (750~850 nm) of Ti-sapphire laser with average transmission above 98.6%, and its surface homogeneity met the requirements of the laser wavefront. The laser induced damage threshold (LIDT) of 2.2 J/cm2 was obtained at 800 nm with the pulse duration of 300 ps for this AR coating on Ti-sapphire crystals, which made it suitable for the optics of ultrashort pulse pico- and femtosecond high power lasers. Further, investigations on the performance of coating solution showed that the viscosity and coating refractive index both increased along with MTEOS prepolymer content, and effect of bake temperature on the latter was very small.
薄膜 溶胶-凝胶方法 激光破坏阈值 增透膜 钛宝石 thin films sol-gel process laser induced damage threshold antireflective coating Ti-sapphire Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2005, 3(1): 127
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800
Porous SiO2 antireflective (AR) coatings are prepared from the colloidal silica solution modified with methyltriethoxysilane (MTES) based on the sol-gel route. The viscosity of modified silica suspensions changes but their stability keeps when MTES is introduced. The refractive indices of modified coatings vary little after bake treatment from 100 to 150 Celsius. The modified silica coatings on Ti:sapphire crystal, owning good homogeneity, display prominent antireflective effect within the laser output waveband (750-850 nm) of Ti:sapphire lasers, with average transmission above 98.6%, and own laser induced damage thresholds (LIDTs) of more than 2.2 J/cm2 at 800 nm with the pulse duration of 300 ps.
310.1210 antireflection 310.3840 materials and process characterization Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2005, 3(1): 244
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Inst. Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, College of Info. Eng., China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018
2 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
3 Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
4 Dept. Mechanical and Electrical, Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, Hangzhou 310012
The thermal stability, Raman spectrum and upconversion properties of Tm^(3+)/Yb^(3+) co-doped new oxyfluoride tellurite glass are investigated. The results show that Tm^(3+)/Yb^(3+) co-doped oxyfluoride tellurite glass possesses good thermal stability, lower phonon energy, and intense upconversion blue luminescence. Under 980-nm laser diode (LD) excitation, the intense blue (475 nm) emission and weak red (649 nm) emission corresponding to the 1G4 -> 3H6 and 1G4 -> 3F4 transitions of Tm^(3+) ions respectively, were simultaneously observed at room temperature. The possible upconversion mechanisms are evaluated. The intense blue upconversion luminescence of Tm^(3+)/Yb^(3+) co-doped oxyfluoride tellurite glass can be used as potential host material for the development of blue upconversion optical devices.
160.4670 optical materials 160.4760 optical properties 160.2750 glass and other amorphous materials 160.2540 fluorescent and luminescent materials Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(9): 09536
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800
Er^(3+)-doped Na2O-WO3-TeO2 glass consistent with standard ion-exchange technology has been fabricated and characterized. The measured absorption and emission spectra of the glass were analyzed by the Judd-Ofelt and McCumber theories. The intensity parameters are Ω2 = 7.01*10^(-20) cm2, Ω4 = 1.80*10^(-20) cm2, Ω6 = 1.03*10^(-20) cm2. The maximum emission cross-section is 0.91*10^(-20) cm2 at 1.533 μm, and a broad 1.5-μm emission spectrum of 65-nm full width at half-maximum (FWHM) is demonstrated. Glass transition temperature, crystallization onset temperature, density, refractive index are also reported for reference in the design and modelling of the ion-exchange process.
160.5690 rare earth doped materials 300.6170 spectra 140.3500 lasers erbium Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(8): 08472





